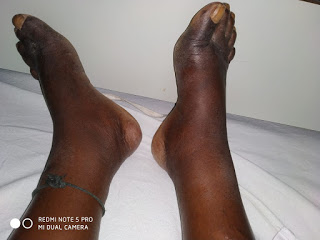
Anasarca
- Pedal edema since 5 days - pitting type
- Abdominal distension
- Facial puffiness
- No urine output since 3 days
- SOB at rest
- Palpitations
Contraindications :
NaHCO3 is contraindicated in patients with metabolic or respiratory alkalosis and in those with hypocalcemia in whom alkalosis may induce tetany, hypochloremia, and hypokalemia. It should also be used with caution in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, because alkalization can reduce the sensitivity of the respiratory regulatory center.
Acute conditions in which sodium bicarbonate therapy doesn’t improve outcomes -
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Lactic acidosis
Septic shock
Cardiac arrest
4. Indications of dialysis in this patient :
Anuria
Urea over 35 Mmol/l
Severe fluid overload
Metabolic acidosis
5. Factors that let to her current condition :
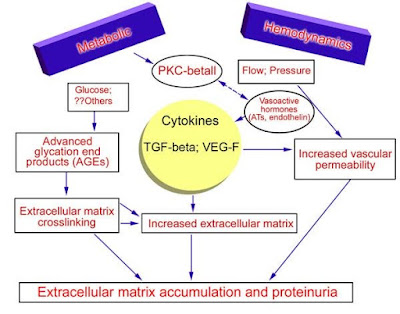
Her renal issues are multifactorial. Her current glomerular injury manifested in nephrotic proteinuria is due to diabetes and hypertension.
She has been chewing tobacco since 8 years which might have caused endothelial injury and adverse cardiac and renal side effects.
Progressive kidney failure can be associated with a gradual decrease of renal and non-renal elimination of nicotine, and this increases the rate of nephrotoxicity. Also, the effects of heavy metals in tobacco like Cadmium (Cd), Mercury (Hg) and Lead (Pb), might be another possible mechanism for tobacco-induced renal damage. However, the mechanism by which tobacco chewing and smoking induces renal damage may be through enhancing the synthesis of free radicals may lead to alter the glomerular function leading to elevated the levels of urea and creatinine in tobacco chewers and smokers.
(https://www.alliedacademies.org/articles/tobacco-chewing-and-smoking-risk-for-renal-diseases.html)
She might have taken NSAIDs that would have precipitated reduced renal perfusion.
Her current condition may also be precipitated by infections.
6. Expected outcomes :
Patients with diabetes and CKD have a lower quality of life and higher health care costs, and face the prospect of end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis. More importantly, this group has an extremely elevated cardiovascular risk and correspondingly reduced survival. Research over several decades has led to two important conclusions. First, progressive worsening of kidney disease is not inevitable in people with diabetes; it can be slowed or even stopped. Second, the elevated cardiovascular risk in this population can be significantly reduced through an aggressive approach to cardiovascular risk factor reduction.
Control of hypertension is of primary importance in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Current guidelines state that the BP goal in patients with diabetes is ≤130/80 mmHg.
Glycemic control is important in this population.
The RENAAL risk score for ESRD emphasizes the importance of identification of level of albuminuria, hypoalbuminemia, increased serum creatinine, and decreased hemoglobin level to predict the development of ESRD in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. Although albuminuria is a very strong predictor for ESRD, the contribution of serum albumin, serum creatinine, and hemoglobin level further enhances the prediction of ESRD.
((https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2650765/))
(https://cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/1/4/761)
7. The patient should be evaluated for cardio renal HFpEF when she develops intermittent paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, orthopnea, dyspnea, fatigue, ascites, and dependent edema.
HFpEF as simply a disease of diastolic function to a reconceptualizing of it as more of a systemic disease, characterized by inflammation and microvasculature dysfunction with adverse sequelae in multiple organs, including, but not limited to, the heart.
Patients with diabetes mellitus were characterized by multimorbidity, left ventricular hypertrophy, impaired chronotropic reserve, and activation of inflammatory, pro-oxidative, vasoconstrictor, and profibrotic pathways.
Both maximal (peak oxygen uptake) and submaximal (6-minute walk distance) exercise capacity were impaired in patients with diabetes mellitus, and hospitalization rates for cardiac or renal causes were increased.
(https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/circulationaha.116.025957)
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0085253819302765)
8. Efficacy of placebo over treatment :
Erythropoietin - The introduction of erythropoietin (Epo) in clinical practice, more than two decades ago, altered completely the management of patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
The extensive use of Epo and its analogues (erythropoietin- stimulating agents, ESAs) for the purpose of anemia correction has succeeded in reduction of associated morbidity and improvement of functionality, exercise tolerance, cognitive function and overall quality of life. Moreover, significant reduction of cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality has occurred.
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3208971/)
(https://cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/2/2/215)
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0272638689801490)
9. Contents of CKDAQ (chronic kidney disease Anemia Questionnaire)
| Symptom/Impact | Number of Items |
|---|---|
| Frequency and severitya | 14 |
| Very tired | 2 |
| Low energy | 2 |
| Weak | 2 |
| Chest pain | 2 |
| Shortness of breath during activity | 2 |
| Shortness of breath while at rest | 2 |
| Difficulty concentrating | 2 |
| Severitya | 1 |
| Bruised skin (past month recall period) | 1 |
| Frequencya | 1 |
| Difficulty remembering things | 1 |
| Impact/ability to do activitiesb | 5 |
| Standing for long periods of time | 1 |
| Sleeping | 1 |
| Didn’t want to do anything | 1 |
| Need to take a break | 1 |
| Need to take a nap | 1 |
| Emotional impactc | 2 |
| Distress | 1 |
| Feel burdensome | 1 |
The Chronic Kidney Disease and Anaemia Questionnaire (CKDAQ) is a 22-item GSK-developed PRO instrument to assess the association with quality of life of patients with chronic kidney disease and anaemia. This questionnaire went through linguistic validation into 71 languages, of which 30 were Asia-Pacific languages. The objective is to identify the challenges raised in performing linguistic validation in these languages; focusing on terminology specific to kidney disease and anaemia, grammatical structure, format, style and register.
(https://jpro.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s41687-020-00215-8)
10. Contribution of protein energy malnutrition to hypoalbuminuria:
Deficient protein intake results in the rapid loss of cellular ribonucleic acid and disaggregation of the endoplasmic reticulum–bound polysomes and, therefore, decreased albumin synthesis.
Kwashiorkor, a severe form of protein-energy malnutrition, presenting in infants and children. They have low serum albumin levels due to a decreased supply of amino acids to the liver as well as other nutritional deficiencies, notably iron and zinc.
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526080/)
SGA in evaluation of malnutrition in CRF patients :
Nutritional assessment of patients with chronic kidney disease is a vital function of health care providers. Subjective Global Assessment (SGA) is a tool that uses 5 components of a medical history (weight change, dietary intake, gastrointestinal symptoms, functional capacity, disease and its relation to nutritional requirements) and 3 components of a brief physical examination (signs of fat and muscle wasting, nutrition-associated alternations in fluid balance) to assess nutritional status.
Poor nutritional status due to protein-energy wasting (PEW) is a common complication associated with increased mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) . Most nutritional markers used in clinical practice are influenced by CKD, co-morbidities or non-nutritional factors such as inflammation, overhydration, and protein losses.
PEW assessed by SGA was found to be an independent predictor of mortality. A range of non-composite nutritional markers could not adequately classify presence of clinically defined poor nutritional status, or explain the variation of SGA status, together with the finding that SGA is a robust prognosticator of clinical outcome, support the value of SGA as assessor of nutritional status in patients with CKD.
(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15483778/)
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5718431/)
————————————————————————————————————————
In a similar case,
(https://bhavyayammanuru.blogspot.com/2020/09/aki-secondary-to-uti.html?m=1)
Case 2:
A 58 year old male presented with the complaints of :
- Reduced urinary output since 3 days associated with burning micturition.
- Anuria since 1 day
- Pain abdomen since 1 day
- Cough not associated with sputum
- Low grade continuous fever not associated with chills







Comments
Post a Comment